利用資訊理論的工作記憶神經編碼實現
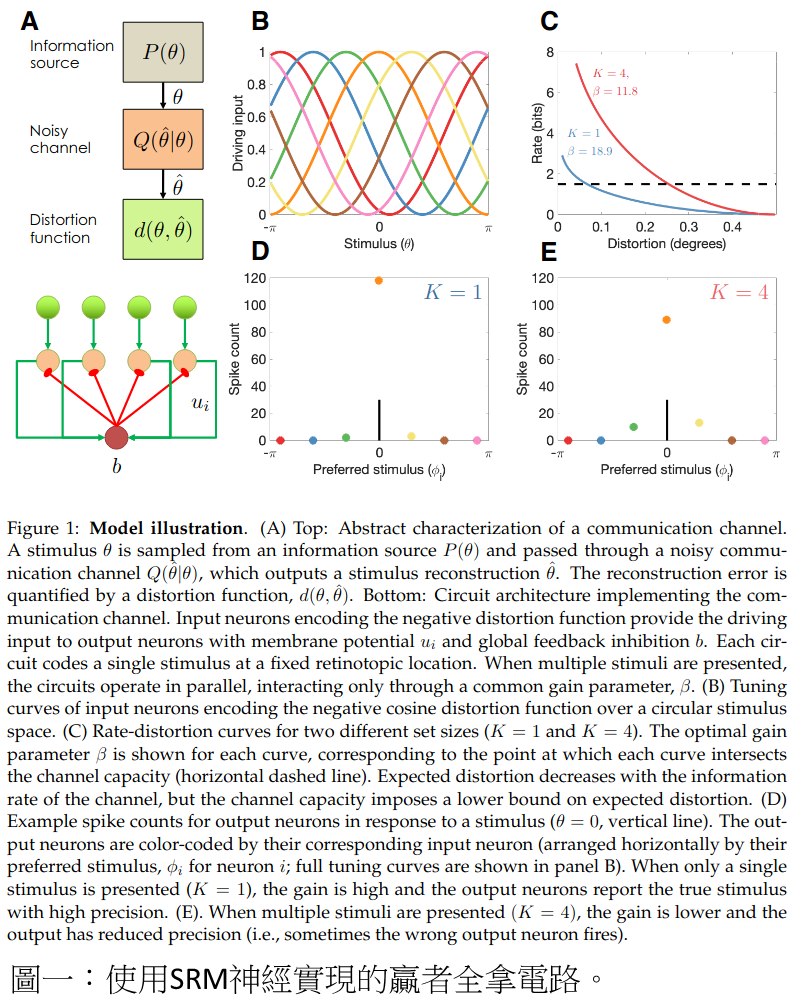
在使用電腦時出現error是一件很煩心的事情;小到日常生活,大到軍事科技,能夠確保訊號正確傳輸是非常重要的。 到了現在,大部分的資料儲存方式都被設計成error很少出現的系統;與之相對的,人腦出錯的機會就大了很多。許多研究(Bates and Jacobs 2020)指出,這是因為人除了傳輸速率跟編碼之外,還需要考慮其他因素的關係,像是要記多少、值不值得注意、會不會花時間等等。 資訊率失真理論(rate-distortion theory)是資訊理論的主要分支,它幫助我們根據通道容量(capacity)跟雜訊(distortion)標準來設計編碼方式。過去已經有研究(Schneegans, Taylor, and Bays 2020)指出,工作記憶(working memory)的性能,是受到族群編碼(population coding)的影響的。 哈佛大學醫學院及腦科學中心在今年二月發表了新的研究(Jakob and Gershman 2022),指出透過調整獲取雜訊通道編碼定理中,獲取最小雜訊的拉格朗日乘數,便能在瞬息萬變的雜訊干擾下調整出最佳傳輸速度。他們也利用了 SRM 神經建造了一個「贏者全拿」(winner-take-all)電路,使得神經們可以在新陳代謝與資料傳輸速度中取得平衡,並根據外界的資訊量進行動態的調整。不過,這個SRM的電路雖與生物實驗的結果一致,電路本身仍然不是仿生的。
撰文|葉宸甫
參考文章
1. Bates, Christopher J., and Robert A. Jacobs. 2020. “Efficient Data Compression in Perception and Perceptual Memory.” Psychological Review 127 (5): 891–917. https://doi.org/10.1037/rev0000197.
2. Jakob, Anthony M. V., and Samuel J. Gershman. 2022. “Rate-Distortion Theory of Neural Coding and Its Implications for Working Memory.” Preprint. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.28.482269.
3. Schneegans, Sebastian, Robert Taylor, and Paul M. Bays. 2020. “Stochastic Sampling Provides a Unifying Account of Visual Working Memory Limits.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 117 (34): 20959–68. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2004306117.


留言
張貼留言